Levels of Theory
What are the three levels of theoretical analysis described by David Marr?
What does Stanovich's system add?
How would you recognize the differences among the levels?
What contribution does this multi-level analysis add to an understanding of behavior and the mind?
How would you apply the analysis to the dual process theory of reasoning?
Levels of Analysis
Computational
What purpose is served by the behavior?
Intentional What are the person’s goals, knowledge, and beliefs? Algorithmic How is the purpose achieved?
Algorithmic What cognitive processes account for these intentions? Implementational
How is the algorithm implemented?
Biological What biological processes operate to make this happen?
Some Important Things to Know
Intentional level - Beliefs and goals
Computational (Functional) Level - Purpose (function)
Algorithmic level - Abstract concepts and mechanisms
Implementation/Biological level - The working entity
Consciousness
What is the difference between a thought experiment and other experiments?
Describe the thought experiments that have been used in discussions of consciousness
How do Daniel Dennett and Patricia Churchland evaluate these experiments?
Some Important Things to Know
The importance of defining terms precisely
Empirical testability as the final arbiter of theoretical arguments
The "need to know" principle - We are not aware of much mental activity
Disgust and other Emotions
According to Kelly's theory, if a person finds eating pet animals to be disgusting, this reflects the conflation of three separate mechanisms. What are they?
How does one account for the fact that some cultures do not find eating pets to be disgusting?
In what way does an understanding of disgust help to explain other emotions?
Some Important Things to Know
Gene-culture coevolution Evolution as a "tinkerer", not an inventor
Co-option - a module becomes adapted to handle an unrelated function Emotions as a method for communication
Emotions in the service of social facilitation
Moral Reasoning
What evidence suggests that deliberate reasoning may not be a determinant of moral reasoning?
What is "moral dumbfounding"? Why is it important?
How does Haidt's theory of morality differ from Kohlberg's
How does Kelly's work on the emotion of disgust clarify the processes involved in moral reasoning?
Some Important Things to Know
Haidt's theory of moral reasoning - Contrasts with earlier theories
Reasoning versus moral intuitions
Priming of moral judgments
Greene and others - There is a role for deliberate reasoning in moral judgments
Social Dilemmas
What is a Nash equilibrium?
What is the "dilemma" in social dilemmas?
In what way is the study of social dilemmas related to work on morality and emotions?
What is Gintis's "choreographer" and how does he, she, or it work?
Some Important Things to Know
Nash equilibrium and the "rational" solution
Superior performance of non-rational strategies
Evolutionary devices: Selfish genes trump selfish individuals
Propensity to acquire social norms that facilitate performance
Reasoning and Rationality
How should we define rationality?
Which normative principle of reasoning does the Linda problem demonstrate?
How can we explain errors on the Linda problem?
What general principles does performance on the Wason problem demonstrate?
Some Important Things to Know
Rationality as consistency
Inadequate definitions: “objective” or “non-emotional”
The conjunction principle
Alternative explanations for errors
Deontic versus non-deontic rules
Dual Process theory
Dual Process Theory
What are the significant differences between the two systems proposed by dual process theory?
What evidence supports dual process theory?
How might deliberate reasoning be involved in moral reasoning?
in social dilemmas?
in emotional responses?
Some Important Things to Know
Goals of the genes versus goals of the individual
Selfish genes versus selfish people
Long leash versus short leaf programming
General-purpose versus modular functions
Double dissociation
System 2 demands on cognitive resources
Theory of Mind
How is pretend play related to theory of mind?
What are the components of Baron-Cohen’s theory?
What evidence supports his theory?
How do simulationist theories of TOM differ from Baron-Cohen’s theory?
Baron-Cohen’s model of the mindreading system.
Some Important Things to Know
Baron-Cohen’s theory
The relevance of autism to the theory
Connections between TOM and consciousness
Representations and meta-representations
ACT-R/PM
What are the components of Anderson’s theory?
What mechanisms or processes are involved in the theory?
ACT-R Components
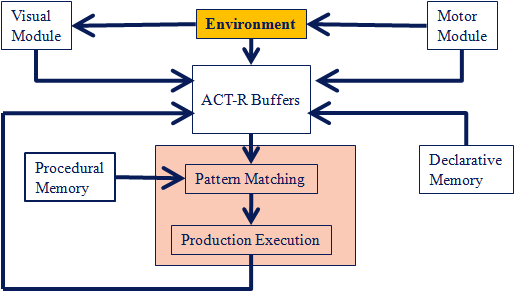
Some Important Things to Know
Association network representations of declarative knowledge, using propositions
Production system representations of procedural knowledge
“Sub-symbolic” processes below the symbolic processes
Goals as controllers of the operations
Modular versus Domain-General Processes
What are they key differences between modular and domain-general processes?
What is the evolutionary justification for modular processes?
What is the difference between modules as proposed by Cosmides and Tooby and modules as defined by Fodor?
What is the dilemma presented by domain-general processes?
Some Important Things to Know
Modules as the way to solve evolutionary problems
Darwinian versus Fodorian modules
Fodor’s argument for the necessity of domain-general processes
Fodor’s claim for the impossibility of explaining domain-general processes